How to Access Task Manager Windows 10?
Are you having trouble accessing Task Manager on your Windows 10 computer? Task Manager is an essential tool for managing and troubleshooting your Windows computer, and it’s important to know how to access it. Thankfully, accessing Task Manager on Windows 10 is a simple process. In this guide, we’ll show you how to access Task Manager on Windows 10 and give you some tips on how to make the most of it.
Task Manager in Windows 10 allows you to monitor the applications, processes and services running on your computer. To access it, you can:
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete keys on your keyboard at the same time.
- Choose Task Manager from the list of options.
- Select the More Details option to expand the list of processes and services.
How to Access and Use the Task Manager in Windows 10
Task Manager is a powerful system monitor and performance optimization tool in Windows 10 that can be used to monitor system applications, processes, and services. It can also be used to optimize system performance, view detailed information about the system, and manage system processes. In this article, we will look at how to access and use the Task Manager in Windows 10.
The Task Manager is a powerful tool that can be used to view detailed information about the system, monitor and manage system processes, and optimize system performance. It can be accessed by pressing the Ctrl + Alt + Del keyboard shortcut or by right-clicking the Windows taskbar. Once the Task Manager is open, it can be used to view detailed information about the system, manage system processes, and optimize system performance.
View Detailed System Information
The Task Manager can be used to view detailed system information, such as the CPU usage, memory usage, disk usage, and network usage. To view this information, open the Task Manager and click on the “Performance” tab. Here, you can view a variety of system performance metrics, such as the CPU, memory, and disk usage. You can also view the network usage in the “Network” tab.
The Task Manager can also be used to view detailed information about the system, such as the number of running processes, the amount of memory used, the amount of disk space used, and the amount of network traffic. To view this information, open the Task Manager and click on the “Details” tab. Here, you can view a variety of detailed system information, such as the number of running processes, the amount of memory used, the amount of disk space used, and the amount of network traffic.
Manage System Processes
The Task Manager can be used to manage system processes, such as terminating processes, suspending processes, and setting process priorities. To manage processes, open the Task Manager and click on the “Processes” tab. Here, you can view a list of all the running processes and their associated process ID. You can terminate a process by right-clicking it and selecting “End Process”. You can suspend a process by right-clicking it and selecting “Suspend Process”. You can also set the process priority by right-clicking it and selecting “Set Priority”.
The Task Manager can also be used to manage applications, such as terminating applications, suspending applications, and setting application priorities. To manage applications, open the Task Manager and click on the “Applications” tab. Here, you can view a list of all the running applications and their associated process ID. You can terminate an application by right-clicking it and selecting “End Task”. You can suspend an application by right-clicking it and selecting “Suspend Task”. You can also set the application priority by right-clicking it and selecting “Set Priority”.
Optimize System Performance
The Task Manager can be used to optimize system performance, such as adjusting the CPU priority level, adjusting the memory priority level, and adjusting the disk priority level. To optimize system performance, open the Task Manager and click on the “Performance” tab. Here, you can view a variety of system performance metrics, such as the CPU, memory, and disk usage. You can adjust the CPU priority level by right-clicking it and selecting “Set Priority”. You can adjust the memory priority level by right-clicking it and selecting “Set Priority”. You can adjust the disk priority level by right-clicking it and selecting “Set Priority”.
The Task Manager can also be used to optimize system performance, such as adjusting the power settings, adjusting the display settings, and adjusting the system settings. To optimize system performance, open the Task Manager and click on the “System” tab. Here, you can view a variety of system settings, such as the power settings, the display settings, and the system settings. You can adjust the power settings by right-clicking it and selecting “Change Settings”. You can adjust the display settings by right-clicking it and selecting “Change Settings”. You can adjust the system settings by right-clicking it and selecting “Change Settings”.
Conclusion
The Task Manager is a powerful tool that can be used to monitor system applications, processes, and services. It can also be used to view detailed information about the system, manage system processes, and optimize system performance. In this article, we looked at how to access and use the Task Manager in Windows 10.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Task Manager in Windows 10?
Task Manager in Windows 10 is an advanced tool that provides users with an overview of running applications, processes, and services on their computer. It also allows users to view and control the usage of their CPU, memory, and other resources. Task Manager can also be used to monitor and manage the performance of their system and to troubleshoot any problems.
Where can I find Task Manager in Windows 10?
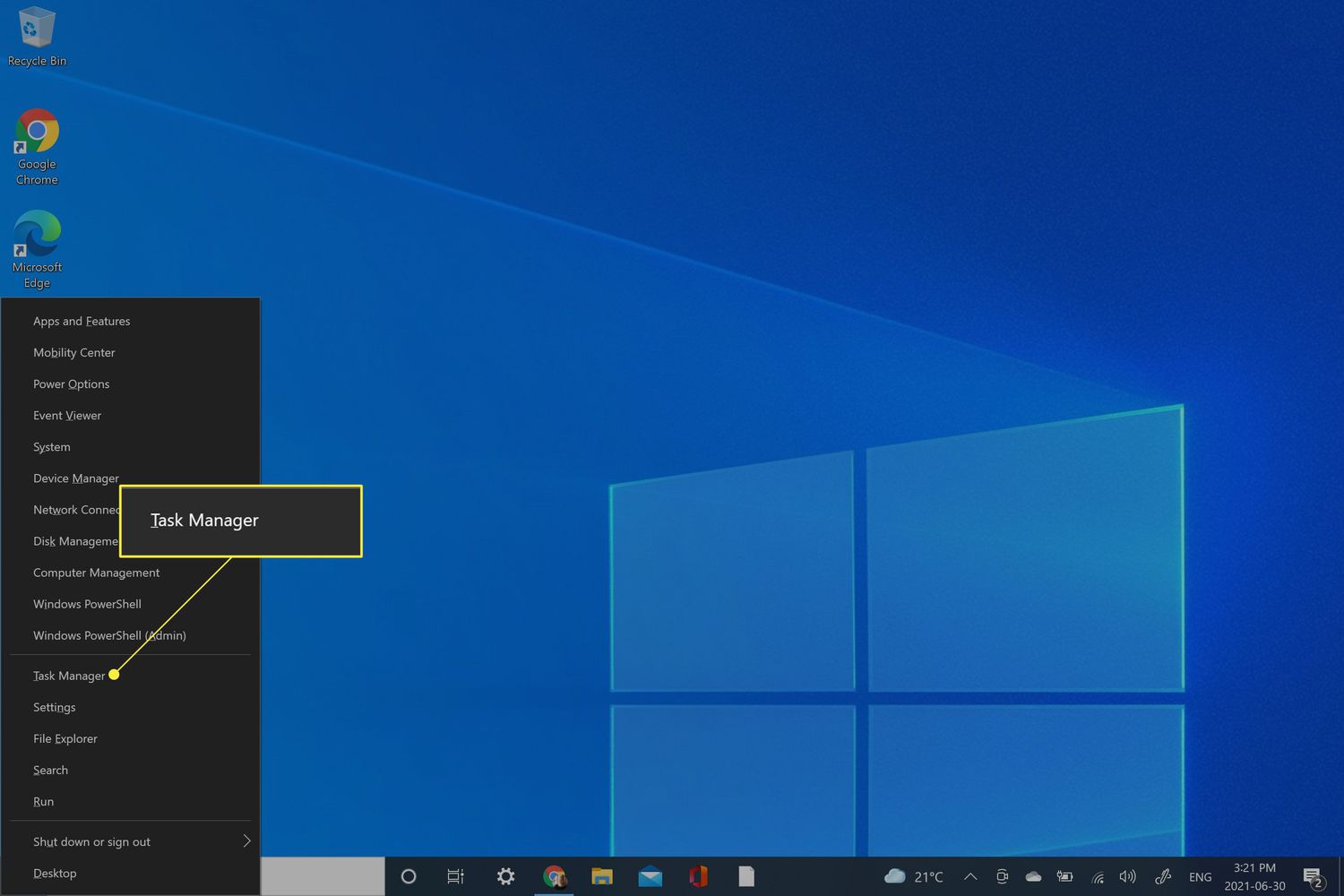
Task Manager can be found in the Start Menu of Windows 10. To access it, simply click the Start button and type “task manager” into the search bar. This will bring up a list of results, and the Task Manager will be the top result. Alternatively, you can also right-click on the Start button and select “Task Manager” from the resulting menu.
How do I open Task Manager in Windows 10?
Once you’ve got the Task Manager open, there are a few different ways to do it. The easiest way is to simply double-click on the Task Manager icon in the Start Menu. Alternatively, you can also right-click on the Start button and select “Task Manager” from the resulting menu. Lastly, you can press the Windows Key + X to bring up the power user options and select Task Manager from there.
What are the features of Task Manager in Windows 10?
Task Manager in Windows 10 has several features that allow users to monitor and manage the performance of their system. These features include the ability to view running processes and services, view hardware resources and usage, monitor performance, and troubleshoot any problems. It also allows users to terminate processes and services, create processes and services, and set priorities for processes.
What are the benefits of using Task Manager in Windows 10?
Using Task Manager in Windows 10 is a great way to monitor and manage the performance of your system. It allows users to view running processes and services, view hardware resources and usage, monitor performance, and troubleshoot any problems. It also allows users to terminate processes and services, create processes and services, and set priorities for processes. This helps users make their system more efficient and reliable.
How can I view more information about a process in Task Manager?
To view more information about a process in Task Manager, simply select the process from the list of running processes and then click the Details tab. This will bring up more detailed information about the process, including its name, description, start time, CPU usage, memory usage, and more.
3 ways to open task manager in Windows #shorts #windows #windows10
Task Manager is an invaluable tool that Windows 10 users should become familiar with. It provides quick access to all sorts of information, such as performance and resource usage. It can also be used to close programs and terminate processes, making it a powerful troubleshooting tool. Learning how to access Task Manager in Windows 10 is easy and can help you unlock the full potential of your computer. With a few simple clicks, you can become an expert in managing processes and applications on your PC.



