How to Use Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
If you’re looking to run a virtual machine on the cloud, Microsoft Azure is one of the best options available. Microsoft Azure’s virtual machines are cost-effective, reliable and secure, making them an ideal choice for businesses of all sizes. In this article, we’ll discuss how to use Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines and explore some of the benefits of this powerful cloud computing platform.
How to Use Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
- Sign up for a Microsoft Azure account or log in if you already have one.
- Select ‘Virtual Machines’ from the left-hand menu.
- Click the ‘Add’ button at the top of the page.
- Choose the Azure subscription and resource group.
- Select the operating system you want to install from the list.
- Choose a VM name and size.
- Configure the optional settings and click ‘OK’.
- Wait for the VM to be created.
- Connect to the VM from the Azure portal.
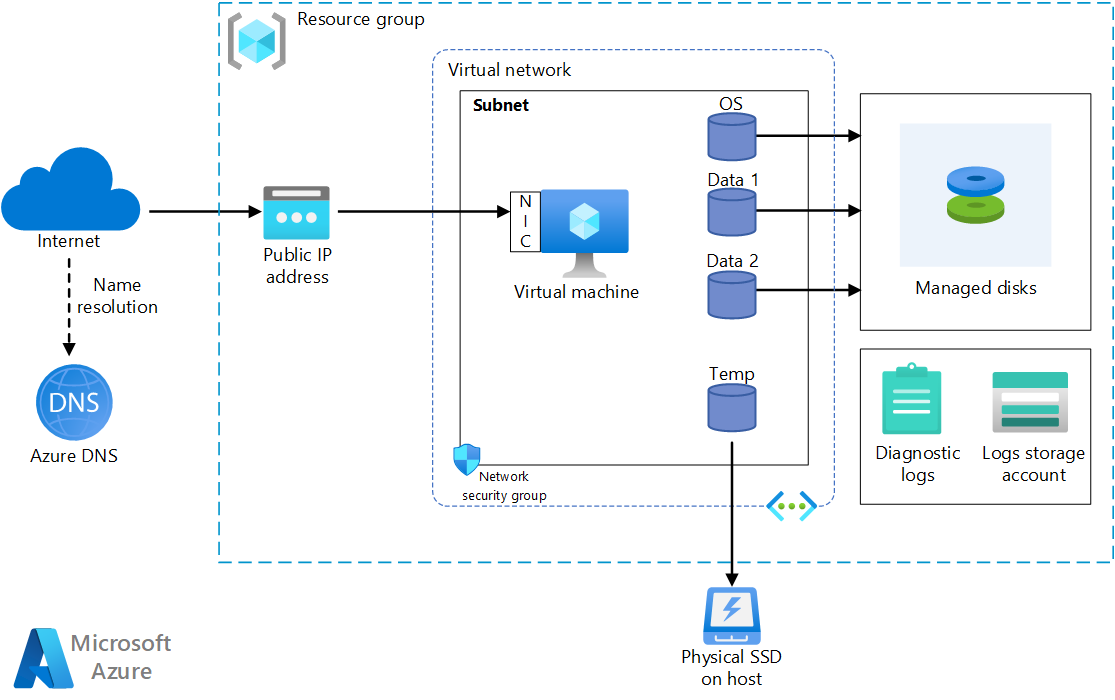
What is Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) are cloud-based computing resources that allow users to create and run virtual machines in Azure’s cloud environment. VMs are used to provide a secure, cost-effective platform for applications, services, and data storage. They are also used to create a highly available and resilient environment for running workloads. With Azure VMs, users can deploy and manage applications in a cloud environment without having to manage physical hardware.
Azure VMs are easily scalable and can be used to create high performance computing clusters. They can be used to run applications and services in a secure, cost-effective manner. Azure VMs also provide a flexible and reliable platform for running web applications, databases, and other services.
Creating an Azure Virtual Machine
Azure VMs can be created using the Azure Portal, the Azure CLI, or the Azure PowerShell. To create a VM using the Azure Portal, the user must first log in to the Azure Portal and select the “Virtual Machines” option. The user then selects the “Create a virtual machine” option and follows the instructions to create a new VM.
The user can also create a VM using the Azure CLI or PowerShell. The user can choose from a variety of templates and images to create the VM. Once the VM is created, the user can configure the VM and install the required applications and services.
Managing an Azure Virtual Machine
Once the VM is created, the user can manage the VM using the Azure Portal, the Azure CLI, or the Azure PowerShell. The user can configure the VM settings, add or remove disks, and attach or detach network interfaces. The user can also start, stop, or restart the VM.
The user can also manage the VM from the command line. The user can use the Azure CLI or PowerShell to manage the VM. The user can use the CLI or PowerShell to create, start, stop, restart, and delete the VM.
Configuring an Azure Virtual Machine
Configuring an Azure VM involves setting up the operating system, applications, and services. The user can configure the VM using the Azure Portal or the Azure CLI or PowerShell. The user can configure the VM settings such as the size, type, and number of CPUs, the amount of RAM, and the number of disks.
The user can also configure the operating system and applications. The user can install the required applications and services on the VM. The user can also configure the network settings, such as the IP address, DNS server, and subnet.
Deploying and Managing Applications on an Azure Virtual Machine
Once the VM is configured, the user can deploy and manage applications on the VM. The user can deploy applications using the Azure Portal, the Azure CLI, or the Azure PowerShell. The user can also use the Azure Marketplace to deploy applications.
The user can also manage the applications on the VM. The user can start, stop, restart, and delete the applications. The user can also manage the application settings, such as the security settings, the application version, and the application configuration.
Monitoring and Optimizing an Azure Virtual Machine
The user can monitor and optimize the VM using the Azure Portal, the Azure CLI, or the Azure PowerShell. The user can view the performance of the VM and the applications running on the VM. The user can also optimize the performance of the VM by adjusting the settings and configurations.
The user can also use the Azure Monitor to monitor the performance of the VM and the applications running on the VM. The user can use the Azure Monitor to view the performance metrics and set alerts for when the performance of the VM or the applications running on the VM falls below a certain threshold.
Related Faq
What is Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine (VM) is a cloud computing service that provides a virtualized environment for users to deploy and manage applications and systems. It is based on the Windows Server operating system and allows users to create, configure, and manage a virtual machine in the cloud. With Azure VM, users can quickly deploy and scale their applications, reduce costs, and increase reliability. Azure VMs also provide users with the flexibility to choose a variety of services and capabilities, including high-performance storage, networking, and security.
How to Create a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Creating a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine (VM) is a straightforward process. First, users will need to log into the Azure portal and select the Virtual Machines option. Then, users will be prompted to select an operating system and choose the size of the VM. Next, users will need to provide a virtual machine name, select an administrative username and password, and create a resource group. Finally, users will need to select a deployment model, configure networking and storage settings, and then review and create the VM.
What are the Steps to Configure a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Configuring a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine (VM) involves several steps. First, users will need to log into the Azure portal and select the Virtual Machines option. Then, users can configure the VM’s hardware settings, such as CPU, RAM, and disk size. After that, users will need to configure the network settings, such as IP address, subnet, and public IP. Finally, users will need to configure the virtual machine’s availability set, storage account, and other settings.
What are the Benefits of Using a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Using a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine (VM) provides users with several benefits. First, users can quickly deploy and scale their applications, reducing costs and increasing reliability. Azure VMs also provide users with the flexibility to choose a variety of services and capabilities, including high-performance storage, networking, and security options. Additionally, Azure VMs are easy to manage and maintain, and can be configured with access and security controls. Finally, Azure VMs offer users the ability to access virtual machines from anywhere in the world, making it ideal for remote work.
What are the Different Types of Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines?
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) come in several different types. These types of VMs include general purpose, compute optimized, memory optimized, storage optimized, and GPU optimized. General purpose VMs are designed for basic workloads such as websites and small databases. Compute optimized VMs are designed for computationally intensive workloads such as batch processing and gaming. Memory optimized VMs are designed for workloads that require high memory capacity and low latency. Storage optimized VMs are designed for workloads with large data sets and high disk throughput. Finally, GPU optimized VMs are designed for workloads that require extreme computational power and support for graphical processing units (GPUs).
How to Monitor a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine?
Monitoring a Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine (VM) is a straightforward process. First, users will need to log into the Azure portal and select the Virtual Machines option. Then, users can select the Monitor tab at the top of the page. This will open the VM’s performance dashboard, which will show users real-time and historical performance data for the VM. Users can also set up alerts to be notified when certain performance thresholds are exceeded. Finally, users can view the VM’s resource usage and configure performance diagnostics to better understand the VM’s performance.
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine is a powerful tool that can help you quickly and easily build, deploy, and manage virtual machines in the cloud. With Azure, you can benefit from the flexibility, scalability, and cost savings associated with cloud computing, as well as the reliability and security that comes with Microsoft’s cloud platform. By taking advantage of the numerous features and tools available, you can maximize the potential of your virtual machines and your business.




